Last updated March 3rd, 2024.
Asia is home to the world’s safest banks. In fact, they’re far better-capitalized than their counterparts in the US.
Yet this wasn’t always true. Not long ago, Switzerland and Liechtenstein were considered the “gold standard” of countries to hold money offshore. Recent events, along with Asia’s rise, have lured capital elsewhere, though.
As such, investors from around the world are looking toward places like Singapore and South Korea to store their assets.
Wealthy investors aren’t just pivoting to Asia because the world’s safest banks are all on the continent; they’re also to diversify their portfolios and hold different currencies.
The Singapore dollar, Korean won, and even a few exotic currencies, including the Thai baht, have significantly outperformed most major global currencies.
Denominating your assets in terms of an appreciating currency is simply a bonus on top of storing money in a stronger bank.
Keeping that in mind, here are the top ten banks in Asia, ranked in terms of their ability to protect customer deposits and provide reliable services.
We hope our list helps you make an informed decision when it comes to diversifying your wealth internationally.
DBS Bank
DBS Bank is the safest bank in Singapore. For over a decade, it has been consistently ranked as the continent’s most secure and reliable financial institution.
As a leading financial services provider, DBS offers its customers a wide range of products and services, including savings accounts, credit cards, loans, investments, and more.
The bank also provides an online banking platform that allows customers to manage their finances securely from anywhere in the world.
With its robust security measures and customer-friendly policies, DBS Bank is a top choice for anyone looking for a safe and reliable banking experience in Asia.
Foreign, non-residents of Singapore can open a bank account at DBS with a minimum deposit of S$350,000 in most circumstances.

Singapore, Asia’s de-facto financial center, continues to take market share from its competitors. Family offices, UHNIs, and multinational firms alike are moving their assets here.
OCBC
A leading institution in Singapore and Southeast Asia, OCBC is the second largest bank in Singapore by total assets and one of the world’s most highly rated banks.
OCBC Bank has provided world-class banking services since 1932, when it was founded as the Overseas Chinese Banking Corporation Limited.
Today, it offers a wide range of products and services, including retail banking, wealth management, and insurance. The bank also operates branches in Malaysia, Indonesia and China.
OCBC provides innovative solutions for its customers through digital technology, such as an AI-driven chatbot.
With its strong presence in Southeast Asia, OCBC is well-positioned for many years to come and is considered one of the most stable banks in Singapore.
If you’re a foreigner without a long-term visa, OCBC usually lets people open an account with a minimum S$200,000 deposit.
United Overseas Bank (UOB)
UOB is a premier banking institution in Singapore, serving customers with diverse financial services and products.
Founded in 1935, UOB has become a major player in the banking industry, with over 500 branches across 18 countries and territories. UOB provides customers with a variety of banking solutions.
It also offers online banking services for customers who prefer to manage their finances online. UOB strives to provide its customers with the best service possible by leveraging technology and innovation to simplify banking processes.
You can generally open a UOB Wealth account as a non-resident, assuming you make a minimum deposit of S$100,000.
Now that the “Lion City’s” major banks have officially cleared the top 3 spots on our list, here’s an article about how you can open a bank account in Singapore as a foreigner.
Korea Development Bank
Established in 1954, the Korea Development Bank (KDB) is a government-owned financial institution that offers various services to governmental organizations and corporations in South Korea.
It was established in 1954 as the first development bank in South Korea, and since then, it has provided loans and other financial services to support the country’s economic growth.
With its strong presence in both domestic and international markets, KDB is considered one of the safest Korean banks.
Export-Import Bank of Korea
The Export-Import Bank (KEXIM) is a well-capitalized, government-funded institution that offers export credit guarantees, loans, and other services to Korean companies.
It was established in 1976 to help Korean exporters and importers finance their trade. KEXIM offers a wide range of services, such as export credit guarantees, loans for overseas investment, foreign currency loans for overseas investment, and more.
KEXIM also provides financial advice to companies looking to expand their business abroad. Its mission is to promote the development of international trade and foreign investments in Korea through its various services.
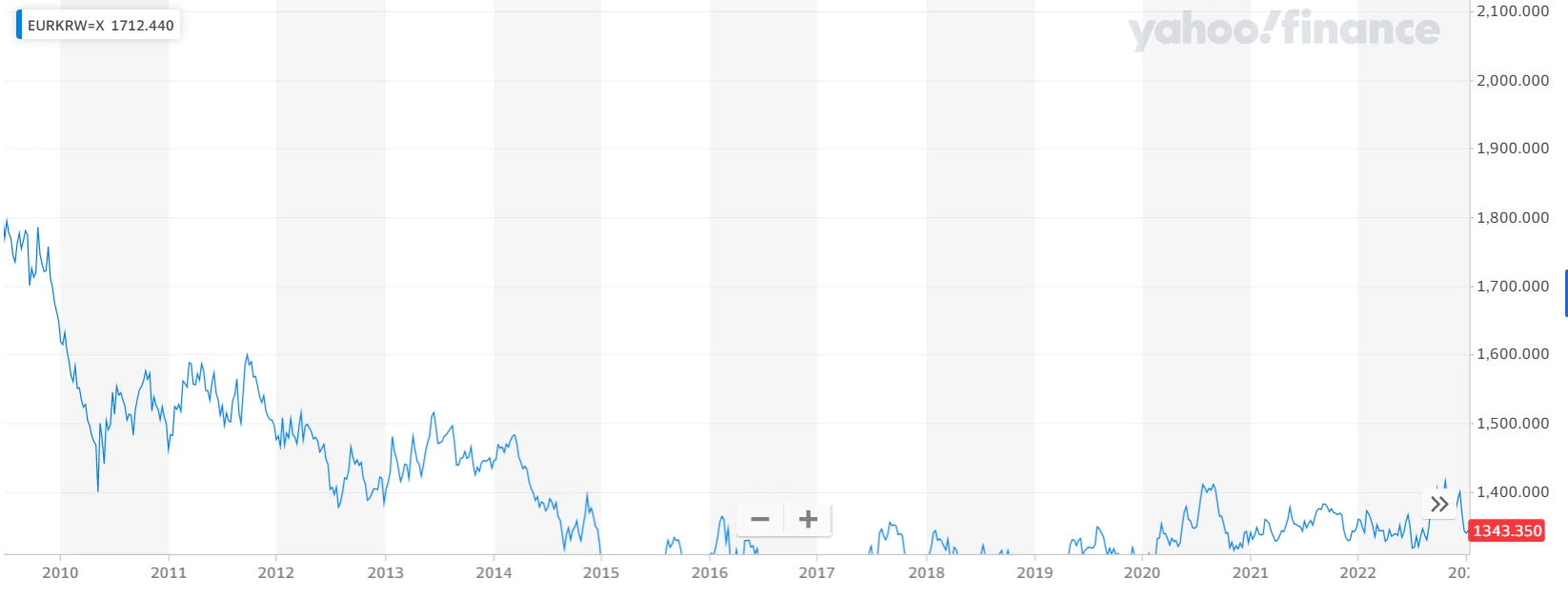
The safest banks in the world aren’t just stable as companies – their host country is too. Local currencies have gained ground in many cases. Here’s a 15-year chart of the Euro compared to the Korean Won, the latter which appreciated heavily.
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK)
The Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) is a leading financial institution in South Korea. It was established in 1954 and has since grown to become one of the largest commercial banks in the country.
IBK provides various services, such as retail banking, corporate banking, investment banking, asset management, and insurance.
In addition to its domestic operations, IBK also has overseas branches in China, Vietnam, Japan, the United States, and other countries.
IBK is also actively involved in philanthropic activities has committed to South Korea’s economic development for decades.
Hang Seng Bank
Hang Seng Bank is one of the largest banks in Asia and generally considered the most stable bank in Hong Kong. Founded in 1933, it has provided services for over 85 years.
They offer deposit accounts, loans, and all the other typical services expected of a large bank. Hang Seng also provides online and mobile banking services that allow customers to manage their finances efficiently.
With its impressive presence in Hong Kong and mainland China, Hang Seng Bank is well-positioned to take advantage of the growing opportunities in these emerging markets.
Bank of Taiwan
The Bank of Taiwan (BOT) is Taiwan’s central bank. Established back in 1899, they’re responsible for issuing currency, managing foreign exchange reserves, and supervising financial institutions – just like any central bank.
Perhaps even more notable? It’s one of the very few central banks in the world that provides general financial services to the public. You’ll find over 150 branches of BOT all across the island.
BOT naturally works with other government agencies to promote economic growth and stability. However, even though it made the 8th spot on our list, we don’t suggest making an investment in Taiwan.
China Development Bank
The China Development Bank (CDB) is a state-owned policy bank of the People’s Republic of China. It was established in 1994 to offer financial services to support the development of the Chinese economy.
The CDB provides loans, equity investments, guarantees, and other financial services for infrastructure and industrial projects.
They have branches in major cities across China and the rest of Asia, as well as offices in Europe, North America, and Africa.
Agricultural Development Bank of China
The Agricultural Development Bank of China (ADBC) is a state-owned financial institution that provides financial services to rural areas and agricultural enterprises. Generally, it’s considered one of the safest banks in China.
Established in 1994, it is the most significant policy bank in China and plays a vital role in providing funds for agricultural development projects.
ADBC is also responsible for implementing national agricultural policies, such as providing loans to farmers, developing rural infrastructure, and improving agritech.
With branches nationwide, ADBC also has a network of foreign partners that it works with to promote international cooperation in the field of agriculture.







